Was this page helpful?
Delegating authentication
SonarQube comes with an onboard user database, as well as the ability to delegate authentication via HTTP Headers, GitHub Authentication, GitLab Authentication, SAML, or LDAP. Each method offers user identity management, group synchronization/mapping, and authentication.
Group mapping
When using group mapping, the following caveats apply regardless of which delegated authentication method is used:
- Membership in synchronized groups will override any membership locally configured in SonarQube at each login
- Membership in a group is synched only if a group with the same name exists in SonarQube
- Membership in the default group
sonar-usersremains (this is a built-in group) even if the group does not exist in the identity provider
When group mapping is configured, the delegated authentication source becomes the only place to manage group membership, and the user's groups are re-fetched with each log-in.
HTTP header authentication
You can delegate user authentication to third-party systems (proxies/servers) using HTTP Header Authentication. See the SSO AUTHENTICATION section within sonar.properties file.
When this feature is activated, SonarQube expects that the authentication is handled prior to any query reaching the server. The tool that handles the authentication should:
- Intercept calls to the SonarQube server
- Take care of the authentication
- Update the HTTP request header with the relevant SonarQube user information
- Re-route the request to SonarQube with the appropriate header information
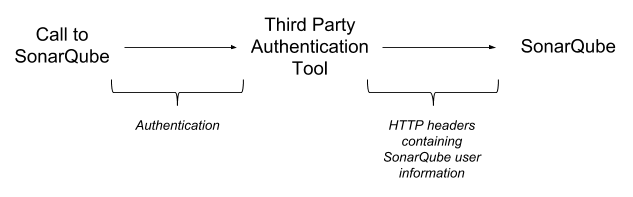
All the parameters required to activate and configure this feature are available in SonarQube server configuration file (in <SONARQUBE_HOME>/conf/sonar.properties).
Using HTTP header authentication is an easy way to integrate your SonarQube deployment with an in-house SSO implementation.
GitHub, GitLab, and Bitbucket Cloud authentication
You can delegate authentication to GitHub, GitLab, or Bitbucket Cloud. See the corresponding DevOps Platform integration page for more information:
SAML authentication
You can delegate authentication to a SAML 2.0 Identity Provider using SAML Authentication.
Example: Using Keycloak as a SAML identity provider
The following example may be useful if you're using Keycloak as a SAML identity provider. If you're not using Keycloak, your settings are likely to be different.
In the Keycloak server, create a new SAML client
Create a new client
- Client ID: Something like "sonarqube", it must not contain whitespace.
- Client Protocol: saml
- Client SAML Endpoint: Can be left empty
Configure the new client
- Under Settings
- Client Signature Required: ON only if the signature of the requests will be active on the SonarQube SAML configuration.
- Encrypt Assertions: ON if the responses from the IdP have to be encrypted.
- Valid Redirect URIs: "/oauth2/callback/saml" (e.g., https://sonarqube.mycompany.com/oauth2/callback/saml).
- Under Keys
- (Optional) Signing Key: Add the service provider private key and the certificate if the signature of the requests is enabled on the SonarQube side (Keycloak generated keys can be used). This private key will have to be provided in PKCS8 format in SonarQube.
- (Optional) Encryption Key: Add the service provider certificate if you want to activate the encryption of Keycloak responses. If request signature is used, you must use the same certificate for the encryption.
- In Client Scopes > Default Client Scopes, remove "role_list" from "Assigned Default Client Scopes" (to prevent the error
com.onelogin.saml2.exception.ValidationError: Found an Attribute element with duplicated Nameduring authentication) - Under Mappers, create a mapper for each user attribute:
- Create a mapper for the login:
- Name: "Login"
- Mapper Type: User Property
- Property: "Username" (note that the login should not contain any special characters other than
.-_@to meet SonarQube restrictions) - SAML Attribute Name: "login"
- Create a mapper for the name:
- Name: "Name"
- Mapper Type: User Property
- Property: "Username" (it can also be another attribute you would previously have specified for the users)
- SAML Attribute Name: "name"
- (Optional) Create a mapper for the email:
- Name: "Email"
- Mapper Type: User Property
- Property: "Email"
- SAML Attribute Name: "email"
- (Optional) Create a mapper for the groups (if you rely on a list of roles defined in "Roles" of the Realm , not in "Roles" of the client):
- Name: "Groups"
- Mapper Type: Role list
- Role Attribute Name: "groups"
- Single Role Attribute: ON
- If you rely on a list of groups defined in "Groups":
- Name: "Groups"
- Mapper Type: Group list
- Role Attribute Name: "groups"
- Single Role Attribute: ON
- Full Group Path: OFF
- Create a mapper for the login:
- In Realm Settings > General > Endpoints, click on "SAML 2.0 Identify Provider Metadata" to obtain the XML configuration file from Keycloak.
In SonarQube, configure SAML authentication
Go to Administration > Configuration > General Settings > Security > SAML
- Enabled: true
- Application ID: The value of the "Client ID" you set in Keycloak (for example "sonarqube")
- Provider ID: The value of the
EntityDescriptor > entityIDattribute in the XML configuration file (e.g., "http://keycloak:8080/auth/realms/sonarqube") - SAML login url: The value of
SingleSignOnService > Locationattribute in the XML configuration file (e.g., "http://keycloak:8080/auth/realms/sonarqube/protocol/saml") - Identity provider certificate: The value you get from Realm Settings > Keys > RS256; click on the Certificate button
- SAML user login attribute: "login" (or whatever you configured above when doing the mapping)
- SAML user name attribute: "name" (or whatever you configured above when doing the mapping)
- (Optional) SAML user email attribute: "email" (or whatever you configured above when doing the mapping)
- (Optional) SAML group attribute "groups" (or whatever you configured above when doing the mapping)
- Sign requests: Set to true to activate the signature of the SAML requests. It needs both the service provider private key and certificate to be set.
- Service provider private key: The service provider private key shared with the identity provider. This key is required for both request signature and response encryption, which can be activated individually. The key should be provided for SonarQube in PKCS8 format without password protection.
- Service provider certificate: The service provider certificate shared with the identity provider in order to activate the requests signature.
You can find here some instructions to convert different key formats.
In the login form, the new button "Log in with SAML" allows users to connect with their SAML account.
SAML and reverse proxy configuration
When using SAML, make sure your reverse proxy is properly configured. See Operating the Server for more information.
LDAP Authentication
You can configure SonarQube authentication and authorization to an LDAP server (including LDAP Service of Active Directory) by configuring the correct values in <SONARQUBE_HOME>/conf/sonar.properties.
The main features are:
- Password checking against the external authentication engine.
- Automatic synchronization of usernames and emails.
- Automatic synchronization of relationships between users and groups (authorization).
- Ability to authenticate against both the external and the internal authentication systems. There is an automatic fallback on SonarQube internal system if the LDAP server is down.
- During the first authentication trial, if the user's password is correct, the SonarQube database is automatically populated with the new user. Each time a user logs into SonarQube, the username, the email and the groups this user belongs to that are refreshed in the SonarQube database. You can choose to have group membership synchronized as well, but this is not the default.
| Apache DS | OpenLDAP | Open DS | Active Directory | |
| Anonymous | Y | Y | Y | |
| Simple | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| LDAPS | Y | Y | Y | |
| DIGEST-MD5 | Y | Y | Y | |
| CRAM-MD5 | Y | Y | Y | |
| GSSAPI | Y |
Y = successfully tested
Setup
- Configure LDAP by editing
<SONARQUBE_HOME>/conf/sonar.properties(see table below). - Restart the SonarQube server and check the log file for:
INFO org.sonar.INFO Security realm: LDAP ...
INFO o.s.p.l.LdapContextFactory Test LDAP connection: OK- Log into SonarQube
- On logout users will be presented a login page (
/sessions/login), where they can choose to login as technical user or a domain user by passing appropriate credentials
From SonarScanners, we recommend using local technical users for authentication against SonarQube Server.
General configuration
| Property | Description | Default value | Required | Example |
sonar.security.realm | Set this to LDAP authenticate first against the external sytem. If the external system is not reachable or if the user is not defined in the external system, authentication will be performed against SonarQube's internal database. | none | Yes | LDAP (only possible value) |
sonar.authenticator.downcase | Set to true when connecting to a LDAP server using a case-insensitive setup. | false | No | |
ldap.url | URL of the LDAP server. If you are using ldaps, you should install the server certificate into the Java truststore. | none | Yes | ldap://localhost:10389 |
ldap.bindDn | The username of an LDAP user to connect (or bind) with. Leave this blank for anonymous access to the LDAP directory. | none | No | cn=sonar,ou=users,o=mycompany |
ldap.bindPassword | The password of the user to connect with. Leave this blank for anonymous access to the LDAP directory. | none | No | secret |
ldap.authentication | Possible values: simple, CRAM-MD5, DIGEST-MD5, GSSAPI. See the tutorial on authentication mechanisms | simple | No | |
ldap.realm | See Digest-MD5 Authentication, CRAM-MD5 Authentication | none | No | example.org |
ldap.contextFactoryClass | Context factory class. | com.sun.jndi.ldap.LdapCtxFactory | No | |
ldap.StartTLS | Enable use of StartTLS | false | No | |
ldap.followReferrals | Follow referrals or not. See Referrals in the JNDI | true |
User mapping
| Property | Description | Default value | Required | Example for Active Directory |
ldap.user.baseDn | Distinguished Name (DN) of the root node in LDAP from which to search for users. | None | Yes | cn=users,dc=example,dc=org |
ldap.user.request | LDAP user request. | (&(objectClass=inetOrgPerson)(uid={login})) | No | (&(objectClass=user)(sAMAccountName={login})) |
ldap.user.realNameAttribute | Attribute in LDAP defining the user’s real name. | cn | No | |
ldap.user.emailAttribute | Attribute in LDAP defining the user’s email. | mail | No |
Group Mapping Only groups (not roles) and static groups (not dynamic groups) are supported. Click here for more information.
For the delegation of authorization, groups must be first defined in SonarQube. Then, the following properties must be defined to allow SonarQube to automatically synchronize the relationships between users and groups.
| Property | Description | Default value | Required | Example for Active Directory |
ldap.group.baseDn | Distinguished Name (DN) of the root node in LDAP from which to search for groups. | none | No | cn=groups,dc=example,dc=org |
ldap.group.request | LDAP group request. | (&(objectClass=groupOfUniqueNames)(uniqueMember={dn})) | No | (&(objectClass=group)(member={dn})) |
ldap.group.idAttribute | Property used to specifiy the attribute to be used for returning the list of user groups in the compatibility mode. | cn | No | sAMAccountName |
Sample configuration
# LDAP configuration
# General Configuration
sonar.security.realm=LDAP
ldap.url=ldap://myserver.mycompany.com
ldap.bindDn=my_bind_dn
ldap.bindPassword=my_bind_password
# User Configuration
ldap.user.baseDn=ou=Users,dc=mycompany,dc=com
ldap.user.request=(&(objectClass=inetOrgPerson)(uid={login}))
ldap.user.realNameAttribute=cn
ldap.user.emailAttribute=mail
# Group Configuration
ldap.group.baseDn=ou=Groups,dc=sonarsource,dc=com
ldap.group.request=(&(objectClass=posixGroup)(memberUid={uid}))Advanced LDAP Topics
Authentication methods
Anonymous- Used when only read-only access to non-protected entries and attributes is needed when binding to the LDAP server.SimpleSimple authentication is not recommended for production deployments not using the ldaps secure protocol since it sends a cleartext password over the network.CRAM-MD5- The Challenge-Response Authentication Method (CRAM) based on the HMAC-MD5 MAC algorithm (RFC 2195).DIGEST-MD5- This is an improvement on the CRAM-MD5 authentication method (RFC 2831).GSSAPI- GSS-API is Generic Security Service API (RFC 2744). One of the most popular security services available for GSS-API is the Kerberos v5, used in Microsoft's Windows 2000 platform.
For a full discussion of LDAP authentication approaches, see RFC 2829 and RFC 2251.
Multiple servers
To configure multiple servers:
# List the different servers
ldap.servers=server1,server2
# Configure server1
ldap.server1.url=ldap://server1:1389
ldap.server1.user.baseDn=dc=dept1,dc=com
...
# Configure server2
ldap.server2.url=ldap://server2:1389
ldap.server2.user.baseDn=dc=dept2,dc=com
...Authentication will be tried on each server, in the order that they are listed in the configuration until one succeeds. User/group mapping will be performed against the first server on which the user is found.
Note that all the LDAP servers must be available while (re)starting the SonarQube server.
Migrate users to a new authentication method
If you are changing your delegated authentication method and migrating existing users from your previous authentication method, you can use the api/users/update_identity_provider web API to update your users' identity provider.
Troubleshooting
- Detailed connection logs (and potential error codes received from LDAP server) are output to SonarQube's
<SONARQUBE_HOME>/logs/web.logwhen logging is inDEBUGmode. - Time out when running SonarQube analysis using LDAP Java parameters are documented here: http://docs.oracle.com/javase/jndi/tutorial/ldap/connect/config.html. Such parameters can be set in
sonar.web.javaAdditionalOptsin<SONARQUBE_HOME>/conf/sonar.properties.
Revoking tokens for deactivated users
When SonarQube authentication is delegated to an external identity provider (LDAP, SAML, GitHub, or GitLab), deactivating a user on the identity provider side does not remove any tokens associated with the user on the SonarQube side. We recommend deactivating the user in SonarQube at Administration > Security > Users by selecting Deactivate from the gear drop-down menu to ensure tokens associated with that user can no longer be used.